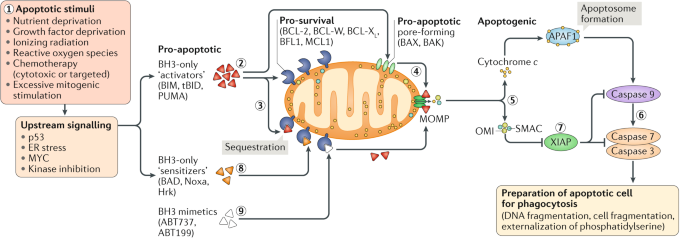
Cancer is a devastating disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth and the ability of cancer cells to evade programmed cell death, known as apoptosis. Apoptosis is a fundamental biological process that eliminates damaged, unnecessary, or dangerous cells from the body. Dysregulation of apoptosis leads to cell survival and accumulation, contributing to tumor development and resistance to therapy. Scientists and researchers have been exploring ways to target and restore apoptotic pathways as a promising strategy for cancer treatment and the Apoptosis Focused Library is taking the lead in this exciting area of research.
The Apoptosis Focused Library is a collection of small molecules designed to selectively modulate the apoptotic machinery and promote programmed cell death in cancer cells. The library is specifically designed to target key components and regulators of the apoptotic pathway, including pro-apoptotic proteins, anti-apoptotic proteins, and key signaling molecules. The compounds in this library are carefully selected and synthesized to enhance their binding affinity, specificity, and potency for their respective targets.
The design of compounds in the Apoptosis Focused Library involves several important considerations:
Target identification and validation: Extensive research is conducted to identify critical proteins and signaling pathways involved in apoptosis. This involves studying the mechanisms of apoptosis, the interactions between pro- and anti-apoptotic proteins, and the dysregulation of these pathways in cancer cells. Validation studies confirm the relevance and therapeutic potential of the identified targets.
Rational drug design: Structural and functional studies of the target proteins provide insights into their three-dimensional structure and active sites. These studies help in identifying binding sites and potential small molecule binding pockets. Computational techniques, such as molecular docking and virtual screening, are employed to identify or design small molecules that can bind to these target sites with high affinity and specificity.
Chemical synthesis and optimization: The identified hits or lead compounds undergo chemical synthesis and optimization to improve their drug-like properties, including solubility, stability, and bioavailability. Medicinal chemistry techniques and structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies are employed to refine the chemical structure of the compounds and enhance their potency and selectivity for the target.
High-throughput screening (HTS): Compounds in the Apoptosis Focused Library undergo HTS to assess their ability to induce apoptosis in cancer cells. HTS assays measure a variety of parameters including cell viability, caspase activation, DNA fragmentation, and mitochondrial membrane potential to identify compounds with pro-apoptotic activity.
Mechanism of action studies: Compounds that show promising pro-apoptotic activity in HTS undergo further studies to understand their precise mechanism of action. This includes investigating their effect on key apoptotic pathways, their interactions with specific target proteins, and their ability to overcome resistance mechanisms.
In vivo and clinical validation: Compounds exhibiting potent pro-apoptotic activity and selectivity in cellular assays move forward for preclinical and clinical validation. Animal studies assess the efficacy, pharmacokinetics, toxicity, and potential side effects of these compounds in vivo. Clinical trials are then conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the promising compounds in cancer patients.
The Apoptosis Focused Library presents an exciting opportunity to explore and exploit the apoptotic pathways for cancer therapy. By specifically targeting the components and regulators of apoptosis, these compounds aim to restore or enhance the programmed cell death process in cancer cells. By inducing apoptosis, these compounds have the potential to eliminate cancer cells selectively while sparing normal cells, thereby offering a more targeted and less toxic therapeutic approach.
In conclusion, the Apoptosis Focused Library represents a significant advancement in cancer research and drug discovery. By focusing on the design and development of compounds that modulate apoptotic pathways, researchers aim to restore the balance between cell survival and cell death in cancer cells. While there is still much to learn about the intricate mechanisms of apoptosis and the optimal strategies for targeting it, the Apoptosis Focused Library offers hope for new and effective treatments that may revolutionize cancer therapy in the future.
Disclaimer: It is important to note that the information provided here is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Consult with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance regarding any medical condition or treatment.