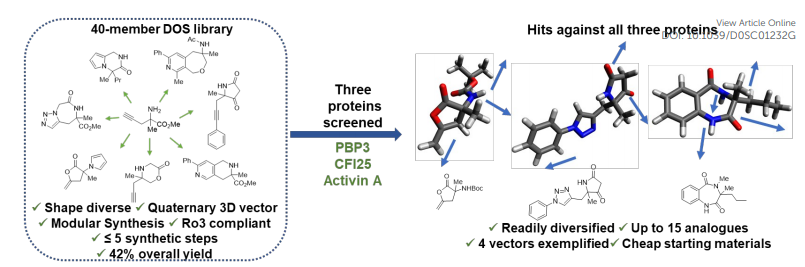
In the field of drug discovery, the search for novel compounds with desirable properties is a constant endeavor. Soluble Diversity Libraries have emerged as a groundbreaking approach, providing researchers with a vast repertoire of small molecules that boast both structural diversity and solubility. In this blog, we will delve into the world of Soluble Diversity Libraries and explore their unique advantages and applications in the quest for innovative therapeutics.
Solubility: A Key Challenge in Drug Development
Solubility plays a crucial role in drug development. Poorly soluble compounds often face challenges in formulation, absorption, and bioavailability, limiting their clinical efficacy. Overcoming solubility issues is essential for improving drug-like properties and enhancing the chances of success in the drug development pipeline.
Understanding Soluble Diversity Libraries
Soluble Diversity Libraries are a valuable resource for researchers seeking soluble compounds with diverse structures. These libraries are specifically designed and synthesized to prioritize solubility while maintaining structural diversity. By carefully selecting building blocks and incorporating solubilizing groups, researchers can expand the chemical space of soluble compounds, allowing for a wider range of potential hits and lead compounds.
Advantages and Applications of Soluble Diversity Libraries
Increased Hit Rates:
Soluble Diversity Libraries significantly increase the chances of identifying hits during the drug discovery process. By emphasizing solubility, these libraries provide a larger pool of compounds that are more likely to exhibit favorable pharmacological activity. This improves the efficiency of screening campaigns and accelerates the identification of promising leads.
Enhanced ADME Properties:
Soluble Diversity Libraries contribute to the optimization of Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion (ADME) properties. By incorporating solubilizing groups and tunable properties, these libraries allow for the quick identification of compounds with improved bioavailability, permeability, and metabolic stability. This facilitates the subsequent stages of drug development and improves the probability of success.
Streamlined Formulation and Development:
The soluble nature of compounds from these libraries simplifies the formulation process. Researchers can focus on optimizing other aspects of drug development, such as dose selection, safety, and route of administration. This expedites the transition from hit identification to preclinical and clinical development.
Exploration of Diverse Chemical Space:
Soluble Diversity Libraries enable exploration of diverse chemical space while maintaining solubility. Researchers can strategically design compounds with varying structural features, introducing new chemical scaffolds and enabling innovative drug design strategies. This expands the repertoire of compounds available for screening and increases the chances of discovering novel therapeutics.
Conclusion:
Soluble Diversity Libraries have revolutionized the field of drug discovery by addressing one of the key challenges: solubility. With their emphasis on solubility and structural diversity, these libraries offer a wealth of compounds that hold great potential for drug development. By increasing hit rates, optimizing ADME properties, streamlining formulation, and exploring diverse chemical space, Soluble Diversity Libraries open up new avenues for innovation and the development of effective therapeutics. As researchers continue to optimize and expand these libraries, we move closer to unlocking innovative solutions and improving patient outcomes in the realm of drug discovery.